티스토리 뷰
출처 : https://www.linuxtechi.com/install-kubernetes-1-7-centos7-rhel7/
How to Install Kubernetes (k8s) 1.7 on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
Kubernetes is a cluster and orchestration engine for docker containers. In other words Kubernetes is an open source software or tool which is used to orchestrate and manage docker containers in cluster environment. Kubernetes is also known as k8s and it was developed by Google and donated to “Cloud Native Computing foundation”
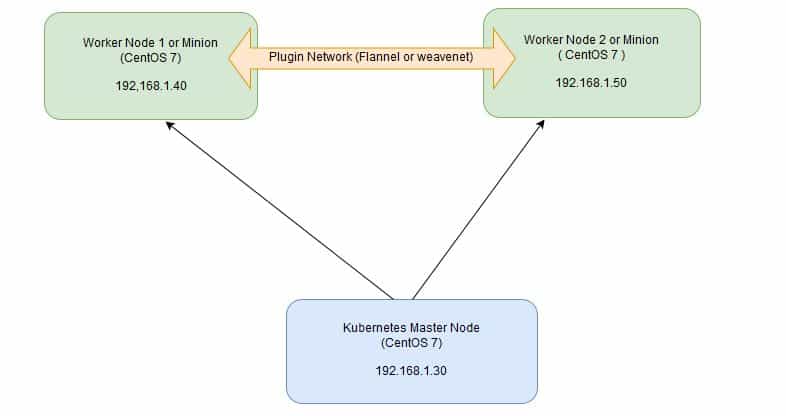
In Kubernetes setup we have one master node and multiple nodes. Cluster nodes is known as worker node or Minion. From the master node we manage the cluster and its nodes using ‘kubeadm‘ and ‘kubectl‘ command.
Kubernetes can be installed and deployed using following methods:
- Minikube ( It is a single node kubernetes cluster)
- Kops ( Multi node kubernetes setup into AWS )
- Kubeadm ( Multi Node Cluster in our own premises)
In this article we will install latest version of Kubernetes 1.7 on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 with kubeadm utility. In my setup I am taking three CentOS 7 servers with minimal installation. One server will acts master node and rest two servers will be minion or worker nodes.
On the Master Node following components will be installed
- API Server – It provides kubernetes API using Jason / Yaml over http, states of API objects are stored in etcd
- Scheduler – It is a program on master node which performs the scheduling tasks like launching containers in worker nodes based on resource availability
- Controller Manager – Main Job of Controller manager is to monitor replication controllers and create pods to maintain desired state.
- etcd – It is a Key value pair data base. It stores configuration data of cluster and cluster state.
- Kubectl utility – It is a command line utility which connects to API Server on port 6443. It is used by administrators to create pods, services etc.
On Worker Nodes following components will be installed
- Kubelet – It is an agent which runs on every worker node, it connects to docker and takes care of creating, starting, deleting containers.
- Kube-Proxy – It routes the traffic to appropriate containers based on ip address and port number of the incoming request. In other words we can say it is used for port translation.
- Pod – Pod can be defined as a multi-tier or group of containers that are deployed on a single worker node or docker host.
Installations Steps of Kubernetes 1.7 on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
Perform the following steps on Master Node
Step 1: Disable SELinux & setup firewall rules
Login to your kubernetes master node and set the hostname and disable selinux using following commands
Set the following firewall rules.
Note: In case you don’t have your own dns server then update /etc/hosts file on master and worker nodes
Step 2: Configure Kubernetes Repository
Kubernetes packages are not available in the default CentOS 7 & RHEL 7 repositories, Use below command to configure its package repositories.
Step 3: Install Kubeadm and Docker
Once the package repositories are configured, run the beneath command to install kubeadm and docker packages.
Start and enable kubectl and docker service
Step 4: Initialize Kubernetes Master with ‘kubeadm init’
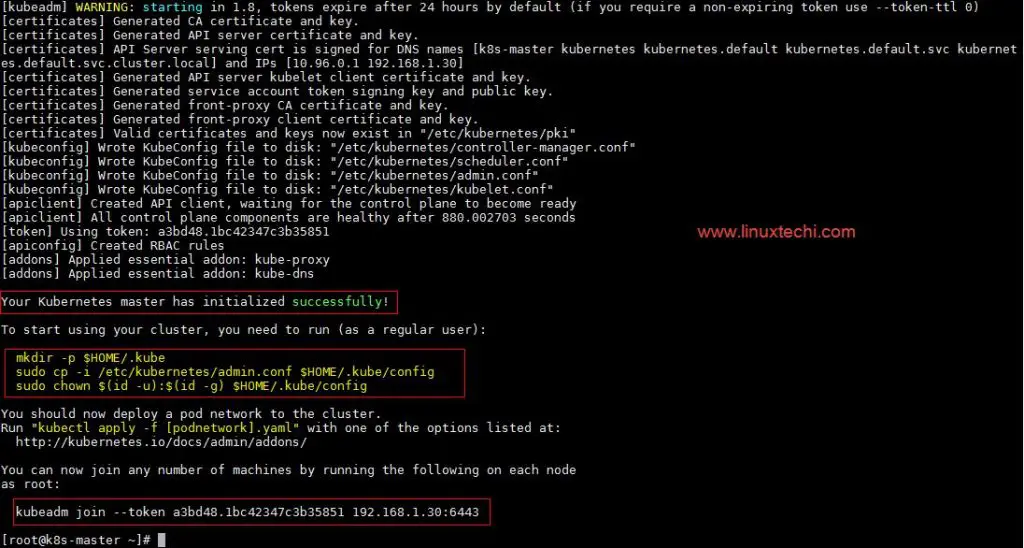
Run the beneath command to initialize and setup kubernetes master.
Output of above command would be something like below
# 여기서 swap 때문에 초기화 안될 수 있다. swapoff -a 으로 SWAP 을 끈다
# 예상으로는 마스터 서버의 반응성을 올리기 위한 조치로 보이며, 마스터 서버의 경우 메모리를 넉넉하게 세팅하는게 필요하다.
As we can see in the output that kubernetes master has been initialized successfully. Execute the beneath commands to use the cluster as root user.
Step 5: Deploy pod network to the cluster
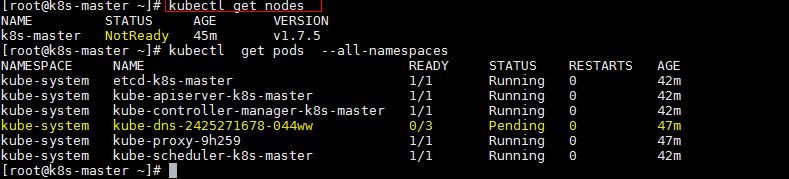
Try to run below commands to get status of cluster and pods.
To make the cluster status ready and kube-dns status running, deploy the pod network so that containers of different host communicated each other. POD network is the overlay network between the worker nodes.
Run the beneath command to deploy network.
Now run the following commands to verify the status
Now let’s add worker nodes to the Kubernetes master nodes.
Perform the following steps on each worker node
Step 1: Disable SELinux & configure firewall rules on both the nodes
Before disabling SELinux set the hostname on the both nodes as ‘worker-node1’ and ‘worker-node2’ respectively
Step 2: Configure Kubernetes Repositories on both worker nodes
Step 3: Install kubeadm and docker package on both nodes
Start and enable docker service
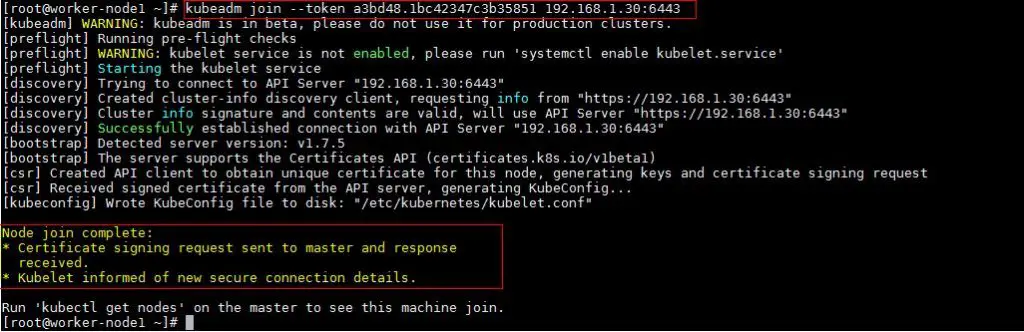
Step 4: Now Join worker nodes to master node
To join worker nodes to Master node, a token is required. Whenever kubernetes master initialized , then in the output we get command and token. Copy that command and run on both nodes.
Output of above command would be something like below
Output would be something like below
Now verify Nodes status from master node using kubectl command
As we can see master and worker nodes are in ready status. This concludes that kubernetes 1.7 has been installed successfully and also we have successfully joined two worker nodes. Now we can create pods and services.
Please share your feedback and comments in case this article helps you to install latest version of kubernetes 1.7